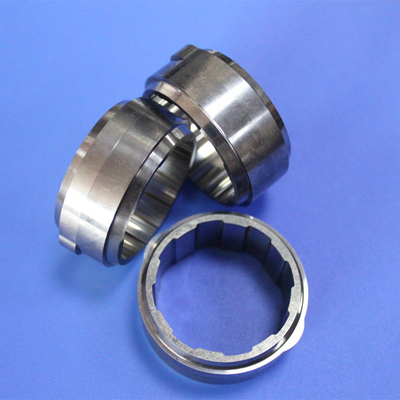
Hardened Steel High-Performance Tungsten Wheel Carbide Rollers
Tungsten wheel carbide rollers are engineered specifically for energy enterprises, delivering high-performance bearing solutions. This comprehensive series includes tungsten carbide magnetic sleeve large bearings, magnetic sleeve bearings, large bearings, upper groove bearings, upper with torque small bearings, thrust sliding bearings, thrust bearings, and additional specialized variants.
Tungsten Carbide Specifications
| Property |
Specification |
| Available Grades |
K20, K10, K30 or other appointed high quality carbide grades |
| Grain Size (µm) |
1.0 ~ 2.0 |
| Cobalt Content (Co%) |
8.0 ~ 10 |
| Density (g/cm³) |
14.41 ~ 14.95 |
| Hardness (HRA) |
89.5 ~ 93 |
| Bending Strength (MPa) |
3200 ~ 4500 |
| Young's Modulus (GPa) |
570 ~ 620 |
| Compressive Strength (MPa) |
4700 |
Non-magnetic carbide material can also be manufactured for forming molds of magnetic materials, offering high hardness, extended service life, superior wear resistance, and strong corrosion resistance.
Key Features
- Diverse Bearing Options: Comprehensive tungsten carbide bearing series includes various models such as large bearings, upper groove bearings, thrust sliding bearings, and others to meet diverse industrial requirements.
- Corrosion and High Temperature Resistance: Tungsten carbide bearings, liners, and sleeves demonstrate exceptional resistance to corrosion and high temperatures, making them suitable for demanding working environments.
- Superior Wear Resistance: The exceptional wear resistance of tungsten carbide ensures prolonged operation in energy production machinery, significantly extending equipment lifespan.
Performance Requirements
For energy production machinery, fundamental requirements include corrosion resistance, high-temperature resistance, and wear resistance. Tungsten carbide bearings provide an ideal solution, meeting these essential requirements while delivering superior performance.
Applications
Tungsten carbide has extensive applications across industrial and jewelry sectors. It is commonly used for hardened tips and cutting edges in drills, end mills, taps, reamers, and other material removal tooling. Additionally, it serves in wear parts including bulldozer blades, excavator teeth, conveyor skip plates, and chute liners due to its exceptional wear resistance.
The material is also utilized in dies and molds that withstand high pressures and repetitive use, and in orthopedic implants such as knee and hip prosthetics for its biocompatibility and mechanical strength. Tungsten carbide is incorporated into drilling tools, oil and gas drilling operations, wind turbine components, and exploration equipment.
Beyond industrial applications, tungsten carbide is processed into particles and grains for coated and bonded abrasives used in polishing and grinding. In the jewelry industry, it is valued for decorative components including rings, cufflinks, and pendants due to its density and distinctive color properties.


 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail! 











