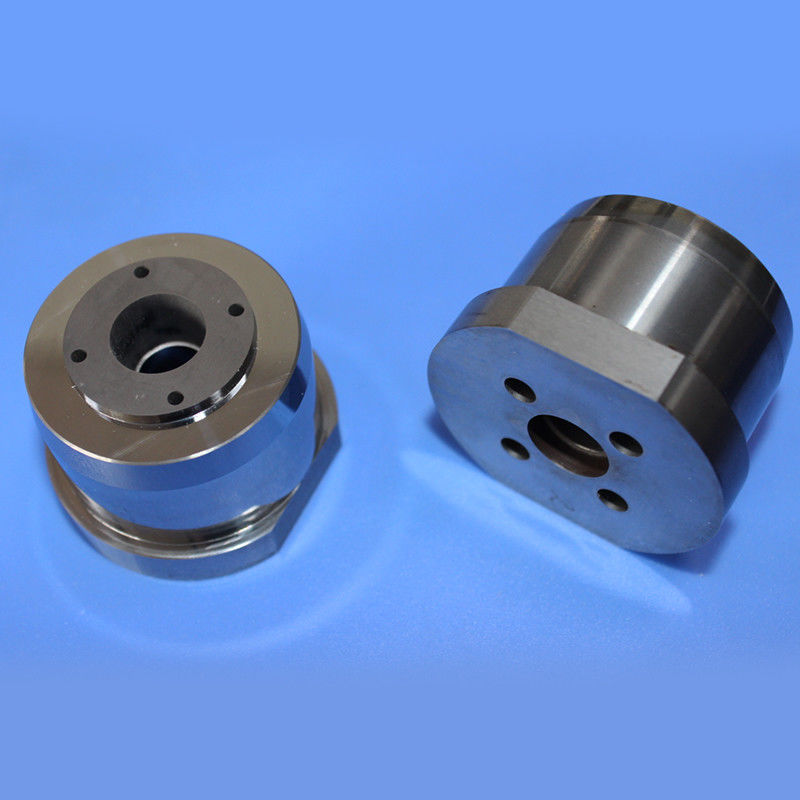
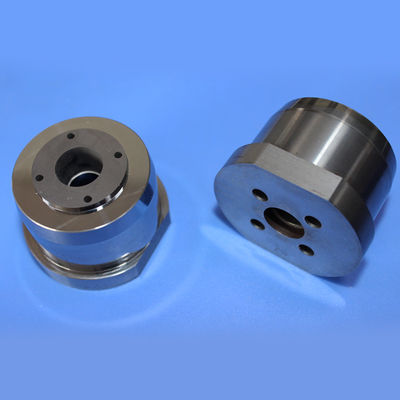
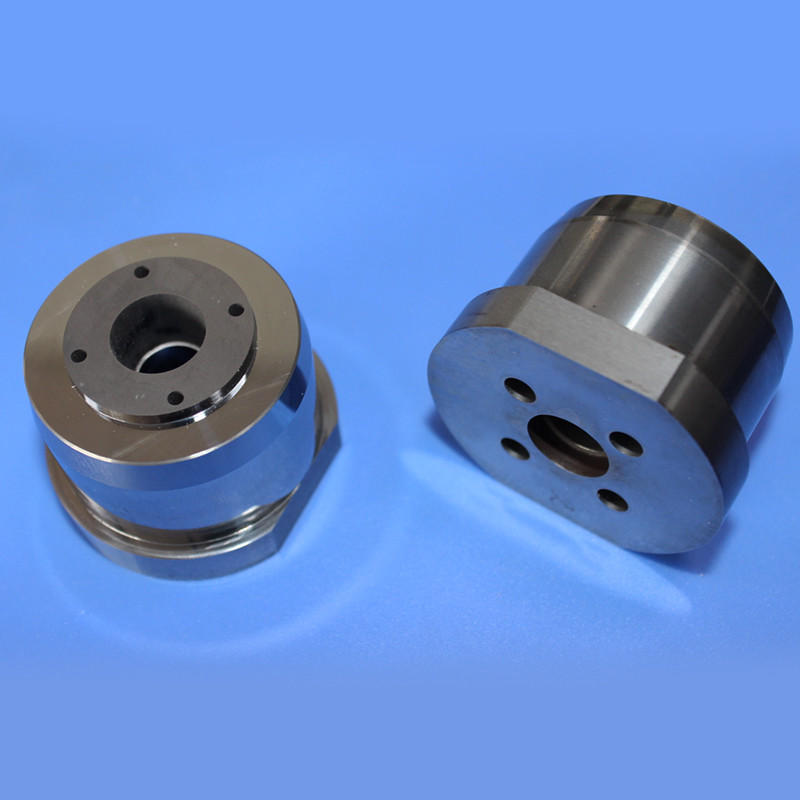
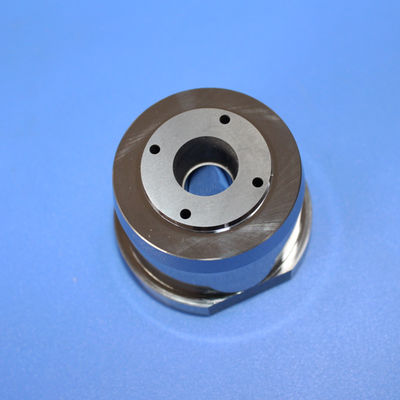
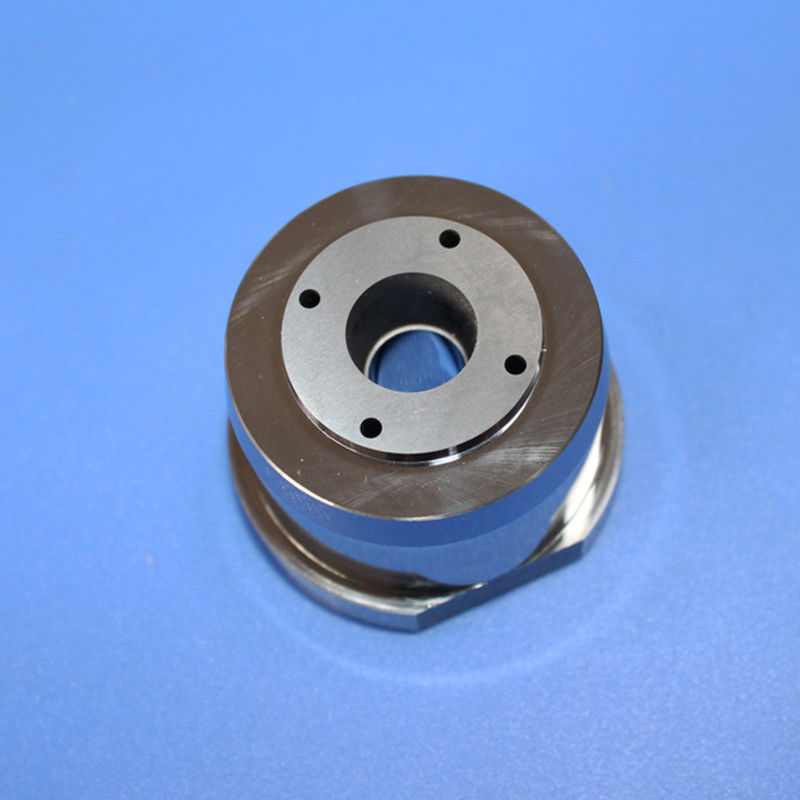
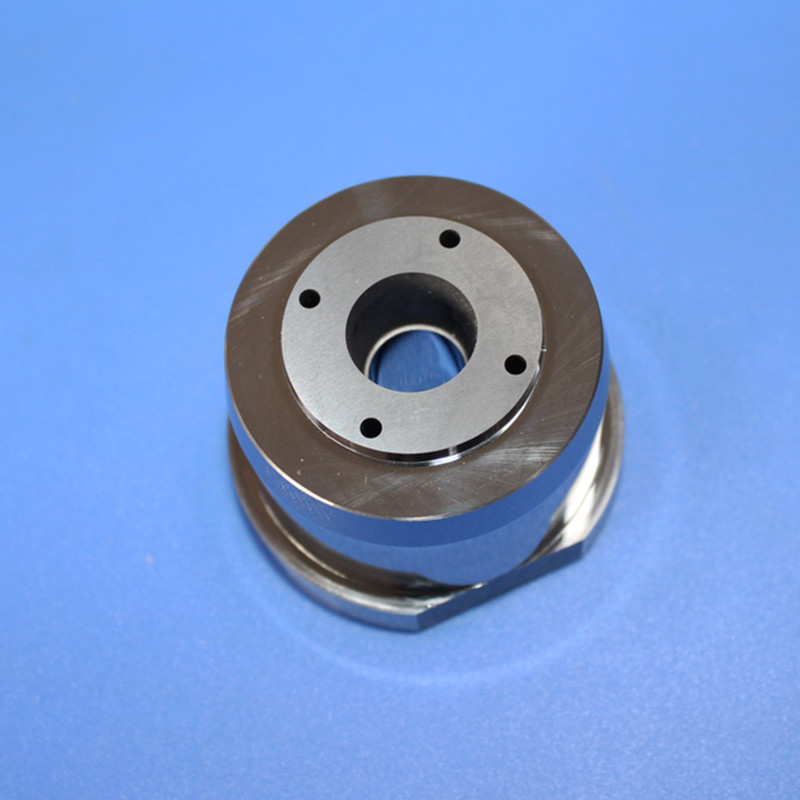
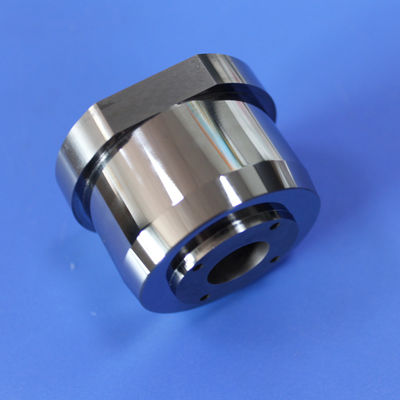
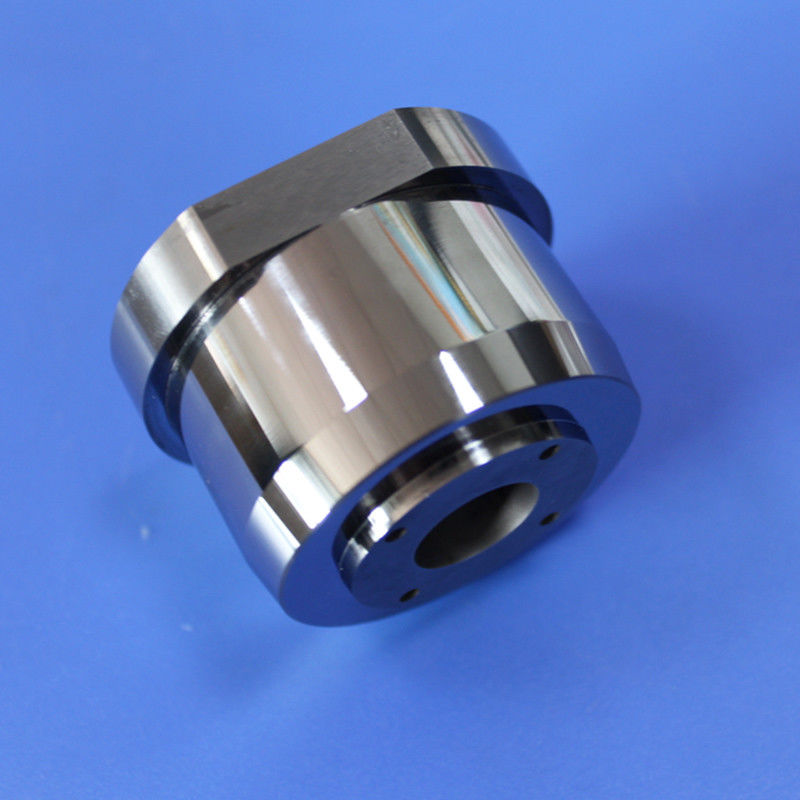
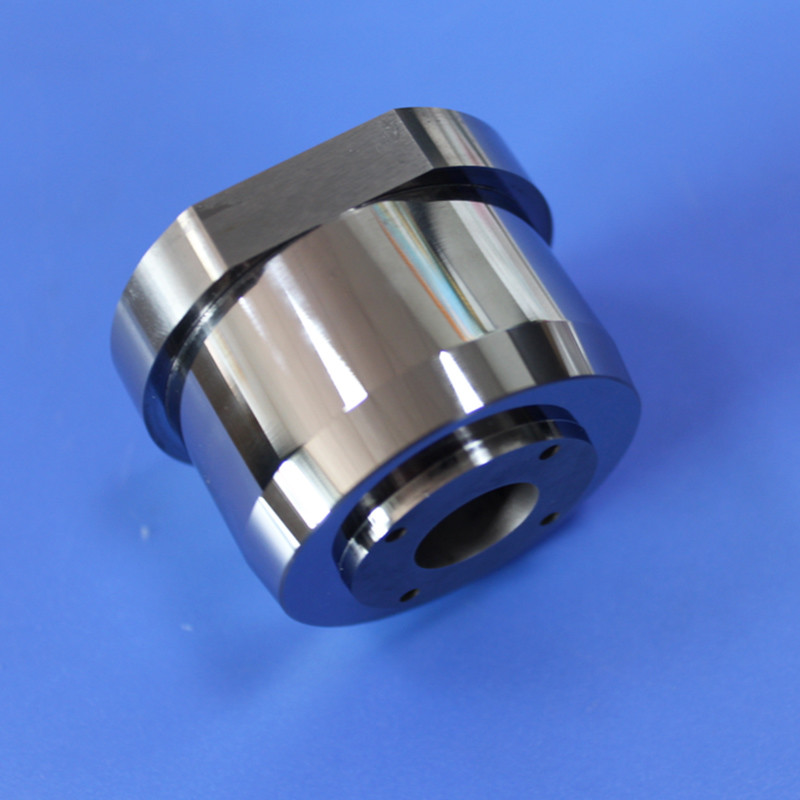
Premium Non-Magnetic Carbide Mold Core with Fixed Tungsten Material
A tungsten steel mold core, also known as a tungsten carbide die core, is a highly durable and wear-resistant jewelry component manufactured by combining tungsten carbide with a metal binder, typically cobalt or non-magnetic nickel.
Material Composition
Tungsten nickel alloys typically contain a high percentage of tungsten (90-97%) and nickel (3-10%), with potential additions of iron or copper to enhance specific properties.
Material Properties
This alloy offers high density, excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, and good corrosion resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty components operating in harsh conditions.
Application Purpose
These blanks serve as starting materials for manufacturing rotor cavities in critical components for rotary engines, turbines, pumps, and compressors. Tungsten nickel alloy rotor cavity blanks ensure robustness, reliability, and longevity in high-performance rotor assemblies, contributing to efficient and durable machinery.
Product Features
Prefabricated Molding Process
This process utilizes pre-designed molds to create components with desired shapes and features, enabling efficient and cost-effective production by directly forming elements like the three-hole design.
Cost Reduction
Prefabricated molding minimizes or eliminates additional machining operations, reducing production costs by saving time, labor, and materials associated with secondary processes like drilling or milling.
Design Flexibility
The process accommodates various complex workpiece designs, including intricate patterns with internal holes and threaded components, enabling production of parts with diverse shapes, sizes, and functionalities.
Enhanced Efficiency
Pre-designed molds ensure consistent and accurate feature replication across multiple workpieces, maintaining quality standards while reducing errors and improving overall production efficiency.
Material Considerations
Material selection is critical for compatibility with molding techniques and meeting final workpiece requirements. Common materials include metals, plastics, composites, and ceramics.
Process Adaptability
Prefabricated molding adapts to various manufacturing methods including injection molding, casting, or extrusion, depending on material, design complexity, production volume, and cost considerations.
Quality Control
Despite cost advantages, comprehensive quality control measures including regular inspections, dimensional checks, and material testing ensure manufactured workpieces meet required specifications and standards.
Technical Parameters
| Grade |
Density (g/cm³) |
Bending Strength (TRS) |
Hardness (HRA or HV) |
Porosity |
Performance and Application |
| SXL03 |
14.95-15.11
15.15-15.35 |
1130-1300 |
91.5 |
|
Good wear resistance; used for small-sized drawing molds |
| SXL06 |
14.88-15.04
14.85-15.05
14.0-14.95 |
1530-1550
1580 |
89.5 |
2.0-1.6 |
Good wear resistance; used for drawing molds of steel (≤20mm) and carbide/non-ferrous metals (≤35mm) |
| SXL08 |
14.65-14.85
14.65-14.85 |
1840-2100 |
89.0 |
2.0-1.6 |
Good toughness and wear resistance; used for drawing molds of steel (≤50mm) and carbide/non-ferrous metals (≤30mm) |
| SXL30 |
14.29-14.49 |
1910 |
HV:1210 |
|
Excellent strength and toughness; used for drawing molds for workpiece pipes and rods |
| SXL50 |
13.86-14.06
13.95-14.15 |
2060-2220 |
86.5 |
|
Excellent strength and toughness; used for drawing molds for workpiece pipes, rods and plates |


 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail! 











